Heat and Work
‣ Example of how heat can create motion
‣ Known for his work in thermodynamics, Joule's experiments demonstrated the relationship between heat and mechanical work, laying the groundwork for the law of conservation of energy.
(1818 – 1889)
James Prescott Joule was an English physicist who studied the nature of heat and helped establish the principle of energy conservation. His discoveries reshaped the understanding of energy in science.
James Prescott Joule's groundbreaking experiment demonstrated the equivalence between heat and work. Using a simple apparatus involving water, a paddle wheel, and a falling weight, Joule observed that as the weight fell and rotated the paddle wheel, the water's temperature rose, suggesting that work could be converted into heat. His findings showed that heat and work are both methods of transferring energy and that they are interchangeable under specific conditions.
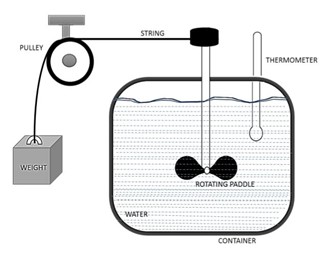
Heat is the transfer of thermal energy.
Work is the transfer of mechanical energy.
Joule’s experiment confirmed that both can produce similar effects, like an increase in temperature when work is done on a system. His experiment showed that when mechanical energy is transferred (work), it can raise the temperature of the system, which is an indication of heat transfer.
Internal energy is the total energy contained in an object, including kinetic and potential energy. Internal energy is a microscopic mechanical energy, the sum of kinetic energies of all its particles and potential energies of interaction among these particles. It depends on its thermodynamic state such as heat transfer and work done. There are many ways to increase the internal energy of a thermodynamic system.
If we add heat to the system and the system does no work, we increase its internal energy. If no heat is added during the expansion or work done by the system against its surroundings, internal energy decreases. And if we remove heat, we reduce the internal energy of the object. Internal energy is also proportional to the change in temperature since heat is also related to it. Thermal energy is related to the kinetic energy or the random motion of molecules and atoms. When an object is heated, the average kinetic energy of the molecules increases and decreases as it is cooled. You may heat the cocoa to increase the temperature or set it aside to decrease the temperature due to energy gained or lost respectively. When both work done and heat transfer occurs;
‣ Example of how heat can create motion